
Sitting For Too Long Can Cause Blood Clots! How to Prevent Deep Venous Thrombosis
Office workers are busy at work, so don’t forget to get up and move regularly. If you sit still for a long time, your blood circulation may be poor, and in severe cases, it may cause blood clots! A civil servant who had been sedentary for a long time was found to have swelling of his lower limbs and skin ulcers. After examination, he was diagnosed with deep vein thrombosis (DVT). What exactly is deep venous thrombosis, and what impact and harm does it have on the body? The following will further introduce the causes, prevention and treatment of deep vein thrombosis.
What is deep vein thrombosis?
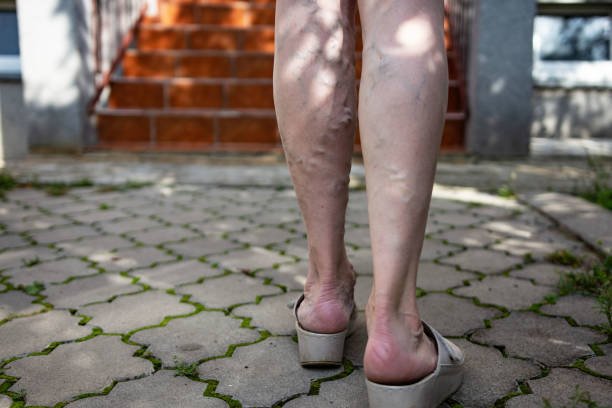
Deep venous thrombosis occurs when a blood clot or thrombus forms in one or more deep veins in the body, usually in the legs, causing leg pain or swelling, or it may not occur. produce any symptoms
Symptoms of deep vein thrombosis
- Swelling in one leg, less common in both legs together
- A painful sensation that usually starts in the calf and feels like a cramp or soreness
- The skin on the legs changes color or turns red
- A hot feeling in the legs
Causes and high-risk groups of deep vein thrombosis
People with special medical conditions, such as poor blood circulation or abnormal blood coagulation caused by taking medications, are more likely to develop deep vein thrombosis. In addition, people who are immobile for a long time, such as bed rest after surgery or accidents, are more likely to develop deep vein thrombosis. , may also occur. People who meet the following conditions are more likely to develop deep venous thrombosis:
- Over 60 years old
- Overweight
- Have the habit of smoking
- Have a history of deep vein thrombosis
- Are taking birth control pills or receiving hormone replacement therapy (HRT)
- People with cancer or heart failure (Heart failure)
- Have varicose veins
Deep vein thrombosis is more likely to occur if:
- Are currently hospitalized or have just been discharged from hospital and are unable to move smoothly
- The state of being confined to bed
- Taking a car or plane for more than three hours
- Are pregnant or have given birth within the past six weeks.
- The body is dehydrated.
However, sometimes deep vein thrombosis can occur suddenly and without warning. If you suspect you have deep vein thrombosis, don’t ignore it. If severe, the blood clot in the vein may break and flow along the blood into the lungs, thereby blocking the blood flow in the lungs, causing a so-called pulmonary embolism, which may be life-threatening. Please ask for help when discovered. Seek medical attention immediately. When you notice the following symptoms, you may have a pulmonary embolism, so be sure to seek medical attention as soon as possible:
- Sudden shortness of breath
- Feeling chest pain or discomfort when taking deep breaths or coughing
- Feeling like you have a slight headache, dizziness, or fainting
- Rapid pulse
- Coughing up blood
5 dietary tips to prevent deep vein thrombosis
- Drink plenty of fluids to keep your blood flowing: Dehydration can cause your body’s blood to become thicker, increasing your risk of blood clots. To keep the body adequately hydrated, girls should get at least about 2,500 grams (g) of water from the food or beverages they eat each day, while boys should get at least Approximately 3,500 grams of water. To measure whether you have replenished enough water, you can judge by the color of your urine. When the urine is light yellow or clear and almost transparent, it means it is normal. However, if the urine is dark yellow or amber, it means you drank too little water.
- Drinking grape juice or red wine can reduce the stickiness of platelets: A study in The Journal of Nutrition pointed out that because purple grapes contain an antioxidant called polyphenols, drinking an appropriate amount of red wine or red wine every day Purple grape juice can help prevent platelets from sticking together and forming blood clots.
- Eating raw garlic to prevent deep vein thrombosis: Research in the Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry points out that garlic has many health benefits, including helping to destroy bad molecules called platelets in the blood. Research shows that to maximize the benefits of garlic, crush raw garlic cloves to release beneficial compounds and eat them raw. If you dare not eat it raw, you can bake it in the oven or boil it in water. The cooking time should be less than three minutes.
- Avoiding bad fats can help circulation in the body: American nutritionist Steven Masley said that eating too much can cause the accumulation of plaque in blood vessels and increase the risk of heart disease and deep vein thrombosis. . According to the American Heart Association, it’s best to avoid trans fats entirely and limit your intake of saturated fat from full-fat dairy products, fat from red meat, sugar and salt, which can cause Inflammation of the body. Therefore, when shopping, you might as well turn to the back of the product to see if there are trans fats in the ingredients. If there are words such as “partially hydrogenated oil” and “hydrogenated oil” in the ingredients, it means that there is some trans fat. In addition, , also pay attention to the sodium and sugar content. Try to choose products with simple ingredients, no trans fat, low sodium and low sugar.
- Use extra virgin olive oil to reduce the risk of embolism: The National Institutes of Health states that eating olive oil at least once a week can reduce platelet activity in obese adults (BMI over 30) who do not smoke. , moderate amounts of olive oil may reduce the risk of blood clots. In addition, a study published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition pointed out that phenols in virgin olive oil are antioxidants that help prevent blood clots. In the study, people who consumed virgin olive oil with high phenolic content had lower levels of substances that promote blood clots.












