Why do Japanese people have the healthiest heart?
Coronary heart disease is called “the first killer of human health”. According to the World Health Organization’s data, the mortality rate of coronary heart disease in Japan is only 0.041%, the lowest in the world. Among males aged 55-64, the mortality rate of Japanese coronary heart disease is less than 1/10 of Americans. According to statistics, the incidence of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases in China is 75 times that of Japan! Their heart-protecting tricks are hidden in their living habits, and we might as well learn from them. Chinese and Japanese people are genetically closely-related and derived their ancestry from a common gene pool. Why is there such a big difference between the two races? This is because the Japanese’s diet and living habits are much much healthier than Chinese people.
1. They love to eat deep-sea fish.
Japan is surrounded by the sea. I eat fish in moderation every day, and the cooking methods are mostly low-temperature cooking, steaming, etc.
Japanese people have been inseparable from fish since childhood. Many studies have proved that eating fish for a long time, especially deep-sea fish such as salmon and tuna, can not only prevent cardiovascular diseases, lower cholesterol, but also reduce cardiovascular diseases by more than 52%. Heart disease patients who often eat fish have a 30% lower mortality rate within two years than those who do not eat fish.

2. Drink green tea
Tea is the favorite of the Japanese. When they drink it, they crush the tea leaves as much as possible, then soak them in water, and drink them together with the tea leaves. This unique habit of drinking tea can make people take in more tea polyphenols, which has a strong protective effect on blood vessels. Green tea has many health benefits, which can reduce the risk of heart disease, inhibit the absorption of cholesterol, reduce bad cholesterol, relieve or delay atherosclerosis, and accelerate fat burning in the body.

3. They like walking
Studies have shown that sitting for a long time can damage the heart, and the chance of blood vessel blockage will increase by 14% for every hour of sitting. Although Japanese cars sell well, Japanese people seldom drive. Whether they own a car or not, most people travel by subway, bus, or bicycle. In this way, even if you are busy at work and have no time to exercise, you can still exercise if you have more opportunities to walk and stand after getting off work.

4. Like to eat natto
Japanese people eat natto just like Chinese people drink soy milk. Natto is indispensable even in nutritional meals in primary and secondary schools, and in welfare homes for the elderly. In Japanese supermarkets, natto is usually displayed together with soy products such as soy milk and tofu. Studies have confirmed that natto has various health effects, such as lowering fat, lowering blood pressure, antithrombotics, strengthening bones and promoting intestinal health. Its most important active ingredient is nattokinase, which has the function of dissolving the thrombus.

5. Eating less salt
According to statistics, the average amount of salt eaten by Japanese people is less than half of that of Chinese people. For all kinds of ingredients, they like to eat raw, cold, boiled, steamed, and refuse heavy tastes. Some gourmets say that Japanese food is wrapped in water, with less oil, less salt, and less condiments, and it tastes healthy and light.

6. They don’t put much oil in cooking
Chinese people like to heat up the oil and stir-fry it in the pan, but the Japanese are very smart when they eat oil. They seldom put oil in their cooking. Most of them are eaten raw, boiled or steamed. After the dishes are cooked, they put a little more oil. Animal oil is basically not used, and vegetable oil is mainly used, including rapeseed oil, olive oil, grape seed oil, etc. Vegetable oil is rich in unsaturated fatty acids, which can reduce platelet aggregation and reduce the incidence of cardiovascular disease. However, after vegetable oil is heated at high temperature, the unsaturated fatty acids in it will be destroyed and no longer have the effect of protecting blood vessels.

7. Eat 30 kinds of ingredients a day
Japanese eat 30 kinds of ingredients a day. This is the dietary goal advocated by the Japanese Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare in the “Guidelines for a Healthy Dietary Life” in 1985. Since then, the concept of 30 kinds of ingredients has spread very widely in Japan, and is used by many housewives as a guideline to arrange a day’s diet.
Some people suspect that it is difficult to eat 30 kinds of ingredients a day, right? In fact, it is not difficult to make snacks. For example, you can cook a pot of healthy multigrain rice with several kinds of grains, and add more ingredients such as soy products, seafood, vegetables, etc. when making soup. There are many types and small portions, and you will be full after eating. This is conducive to nutritional balance and weight control.

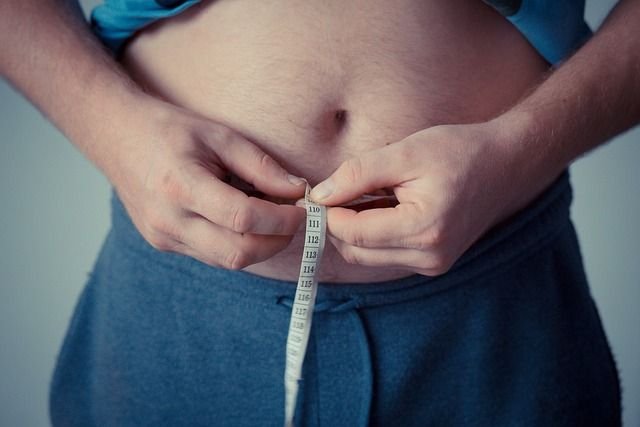
8. Control the waistline
The research found that people with thick waistlines are about 40% more likely to suffer from heart disease than others, especially middle-aged men with big bellies are more likely to die suddenly. Japanese law stipulates that companies must check the waist circumference of employees aged 40 to 75 every year: the waist circumference of men must not exceed 85 cm, and the waist circumference of women must not exceed 90 cm.
Those whose waist circumference exceeds the standard must check blood pressure, blood sugar, and blood lipids. If one of them fails, they will be included in the risk group of metabolic syndrome. If two of them fail, they will be listed as patients with metabolic syndrome. Companies will also face fines from the government if they fail to manage their employees’ waistlines and weights.
Therefore, the waistline of the Japanese is the smallest in the world. Except for some sumo wrestlers, there are almost no fat people on the street.

9. Love cleanliness
Why do we say that? It can be seen from this point that Japanese toothpaste consumption ranks first in the world. Studies have found that reducing oral periodontal bacteria can slow down and prevent cardiovascular diseases, such as arteriosclerosis. Well, regular brushing, flossing, and regular oral health maintenance can protect against heart disease.
After controlling for other factors, the researchers found that those who admitted to brushing their teeth infrequently had a 70 percent higher risk of heart disease. Poor oral hygiene is the main cause of gum infection, periodontal disease, which can increase the burden of personal inflammation and increase cardiovascular risk.

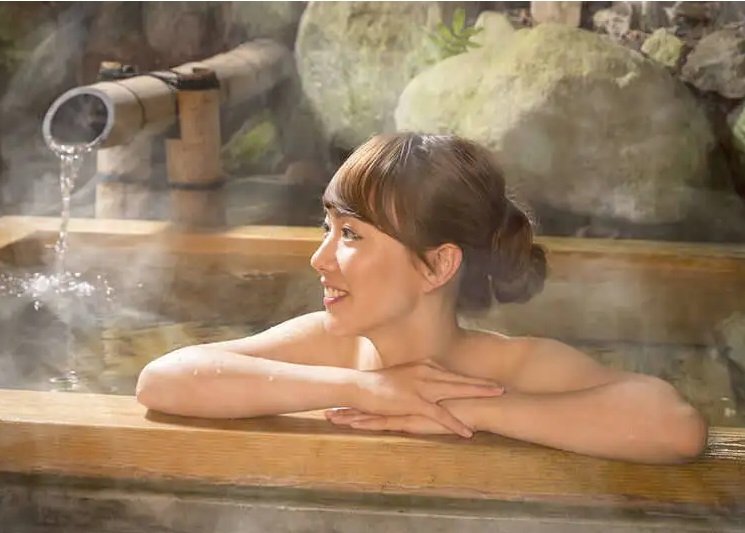
10. They will relax after work
When they return home after work, most Japanese people take a bath, and go to hot springs on holidays. Even if the house is not big, with forty or fifty square meters, the family will buy a small bathtub, which is only enough for one person to squat in it. After taking a shower, the whole family takes turns to enter the bathtub, and soak for 20 minutes each, which can not only dilate the capillaries, but also release the stress of the day and fully relax.

Related Article of Heart Diseases
Top 6 Foods to Lower Your Bad Cholesterol
The Best Fruit To Avoid Heart Disease
What is the Cause of Arteriosclerosis?
Wonderful 10 Foods to Lower Blood Pressure
Reference
Book Recommodation
Supplement For Heart Diseases
-
Benefit of Vitamin C & Bioflavonoids
- Enhance immune function, prevent colds It can help white blood cells fight bacteria and viruses and enhance immunity.
- Promote wound healing It is a nutrient required for collagen production. Collagen is an important component of connective tissue, which can maintain a tight arrangement between cells and promote skin wound healing.
- Whitening, anti-aging, skin health.
- Anti-cancer, antioxidant.
- Delay the occurrence of cataracts.
- Prevent cardiovascular disease.
-
1. Maintain Heart Health
2. Treat Mental Illness
3. Help Lose Weight
4. Support eye health
5. Relieve rheumatoid arthritis symptoms
6. Maintain skin health
7. Helps baby vision and hand-eye coordination
8. Reduce liver fat
9. Improve symptoms of depression
10. Improve ADHD in children
11.Improve memory in the elderly
12. Improve asthma symptoms and allergy risk
13. Improve bone health -
Benefit of Vitamin E
- Reduce the oxidation of unsaturated fatty acids
- Helps maintain cell membrane integrity
- Antioxidant
- Improve skin and blood cell health
- Helps reduce free radical production
- Improve your chances of getting pregnant
- Maintain youthful energy
- Maintain health
- Stay away from sensitive conditions
- Promote circulation in the body
- Regulate physiology
- Good for female fertility
-
- Helps maintain the normal secretion of thyroid hormones.
- Helps maintain normal growth, development, neuromuscular function.
- Regulates cellular oxidation.
- Improves cognitive memory function (under stress)
- Benefits phenylketonuria
- Good for depression
- Benefits schizophrenia
- Improves narcolepsy/narcolepsy
- Can improve human immune function.
- Can prevent cancer and fight cancer.
- Can protect the heart muscle.
- Protects the liver.
- Is an antioxidant.
- Can be involved in the treatment of diabetes.
- Protects and repairs cells.
- Improve vision and prevent eye diseases