Should I Need an Electrocardiogram or X-ray for Heart Discomfort? Learn About Various Heart Examination Items
Heart disease generally refers to all diseases that affect the heart. Different types of heart examinations have their own advantages and disadvantages. Doctors will choose the examination method that suits you based on professional judgment. The following heart examination methods are divided into invasive and non-invasive. Introduction to two categories.
Non-invasive examination
1.Blood test
Blood is drawn from a vein to check the substances contained in the blood. The test may require the subject to fast for 12 hours before taking it. Generally speaking, a blood draw for heart disease may include testing for the following values:
Blood is drawn from a vein to check the substances contained in the blood. The test may require the subject to fast for 12 hours before taking it. Generally speaking, a blood draw for heart disease may include testing for the following values:
- Total cholesterol
- Low-density lipoprotein (LDL)
- High-density lipoprotein (HDL)
- Triglyceride
- Lipoprotein(a) (Lp(a))
- C-reactive protein (CRP)
- Homocysteine
2.Electrocardiogram
Electrocardiography (EKG or ECG) is a non-invasive test that can detect the electrical activity of the heart to help doctors determine whether the subject’s heart has arrhythmia or other heart problems. The detection method of electrocardiogram is quite simple. Just stick the electrode patch on the chest of the subject, and the electrocardiogram instrument can detect the heart activity.
3.Exercise electrocardiogram
Exercise electrocardiography is a stress test on the heart. By asking the subject to operate a treadmill or flywheel, the state of the heart can be observed during exercise. By recording changes in the subject’s blood pressure and heartbeat, we can learn whether the subject has ischemic heart disease or arrhythmia. Additionally, in some cases, heart rate-increasing drugs may be used instead of exercise to simulate the heart’s response to exercise.
Just like the electrocardiogram, the subject also needs to wear electrode patches, and after measuring the blood pressure, keep exercising for a certain period of time as instructed by the doctor. If the subject feels obvious discomfort during the procedure, please inform the physician.

4.Holter 24-hour continuous ECG
Holter monitor, which is a portable electrocardiogram device that continuously records the subject’s heartbeat status within 24 hours, making up for occasional arrhythmia or chest pain symptoms that cannot be observed with a single electrocardiogram. Depending on the situation, the subject may also receive continuous ECG for 48 or 72 hours.
After the test subjects go to the hospital to install the Huote electrocardiogram device, they can return home. During the test period, it is not advisable to engage in a lot of activities to avoid excessive sweating, and you cannot take a bath to avoid affecting the test results.
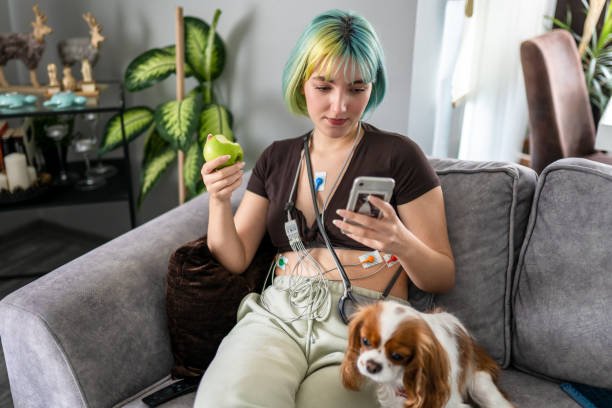

5.Cardiac event recorder
Also a portable device, the cardiac event recorder is suitable for patients with low frequency of symptom attacks. It is used to record the patient’s heart activity when uncomfortable symptoms occur. Therefore, unlike a continuous ECG, the cardiac event recorder does not continue to record heartbeats unless the user presses the “record button”.
The cardiac event recorder is usually worn for more than one week. During the process, the subject can remove the device and take a shower.
6.Cardiac ultrasound
Echocardiography is operated by a doctor holding an ultrasound probe, gently pressing it on the subject’s chest and moving it. Based on the speed of the ultrasound waves bouncing around the heart, relevant data can be presented for the doctor to understand the heart. Valve, heartbeat function, and heart structure problems.
In addition, the subject may also need to adjust their posture or perform a specific breathing method according to the doctor’s instructions during the process to facilitate the test.
7.Chest X-ray
The condition of the heart and lungs can be seen through X-ray equipment. Chest X-rays are not only used for heart examinations. The condition of various organs or bones in the body can be understood through X-ray examinations. Since only flat images can be observed, they are sometimes taken from the side or other angles to facilitate the physician’s assessment. Generally speaking, a chest X-ray will absorb about 0.1 millisieverts of radiation.
8.Cardiac computed tomography
Computed tomography (CT) uses continuous X-ray scans at different angles to take images of the heart, which can more clearly see whether there is any blockage in the coronary arteries. However, the amount of radiation received in one tomography scan is about 7 millisieverts. Much higher than a chest X-ray.
9.Cardiac MRI
Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) uses magnetic fields and radio waves to create detailed images of the heart. During the examination, you lie in a long tubular machine. It uses magnetic fields and radio waves to create detailed images of the heart. , so that the doctor can observe.
MRI can provide multi-section images without any radiation concerns. Compared with tomography, MRI is easier to observe whether there are lesions in the soft tissue of the heart. The disadvantage is that the examination process is long, and if the subject has metal implants in his body, he may not be able to undergo MRI examination.
10.Nuclear medicine examination
Nuclear medicine examination is also called myocardial perfusion scan. This method is through intravenous injection of nuclear medicine examination preparations such as thallium-201 (Tl-201) and TC-99m (TC-99m), and then uses single-photon computed tomography A scan (SPECT) looks at how blood flows through various parts of the heart. This test is mainly used to check whether the subject’s coronary arteries are blocked or narrowed.
In addition, myocardial perfusion scans are often paired with stress detection, because during exercise, coronary blood flow increases to supply sufficient oxygen to the myocardium, which can easily reveal whether the subject has arterial blockage.
Invasive examination
1.Cardiac catheterization
Cardiac catheterization, including coronary angiography, is an invasive examination. The main method of operation is to insert a thin tube from the groin or wrist, inject contrast agent into the blood vessels, and use X-ray equipment to observe the blood flow of the coronary arteries. In addition, cardiac catheterization can also be used in coronary artery balloon dilatation and vascular stent placement.
People who require cardiac catheterization may have undergone other non-invasive tests, but the detailed cause still cannot be found. Cardiac catheterization can help doctors better observe whether the subject’s heart has congenital defects, valves, or coronary artery problems. If necessary, doctors can also use cardiac catheters to treat patients directly.

2.Cardiac electrical physiological examination
Electrophysiology Study can detect the electrical activity of the heart and, under control, send out electric current to stimulate the heart to find out the possible causes and treatments of arrhythmia. Its operation method is also the concept of a concentric catheter, in which electrode leads are inserted from the groin and connected to the heart. For lesions causing abnormal heart rhythms, doctors may use radiofrequency catheter ablation (RFCA) to interrupt abnormal electrical conduction and return the heartbeat to normal.