Does Arterial Calcification Make Arteries Hard? Vascular Calcification Has Nothing to Do With Eating Calcium! Quit Smoking and Drinking, and Eat Healthily
Most people may have heard of atherosclerosis, and vascular calcification is a very important indicator of arteriosclerosis. The higher the calcification index of vascular calcification, the more serious the degree of arteriosclerosis. If you belong to the group of people who have high levels of obesity, are obese, smoke and drink a lot, or have kidney disease, then cardiovascular calcification may come to you at any time! What exactly is vascular calcification? Is eating too much calcium tablets related to vascular calcification? Let this article tell you.
What is vascular calcification? Will eating too many calcium tablets have any effects?
It is a long-standing myth that eating too much calcium tablets leads to vascular calcification (Dystrophic calcification). Calcium supplements in the general diet will not cause vascular calcification, because in order to maintain human body functions, bones will naturally weaken when the calcium ion concentration is low. Releases calcium ions into the blood to maintain blood calcium balance. Therefore, even if you supplement more calcium, the body will still maintain blood calcium balance and will not directly lead to vascular calcification.
In addition, too much vitamin D and phosphorus can also cause excessive calcium deposition on blood vessel walls (for example, patients with kidney disease cannot metabolize phosphorus in the body), further leading to the risk of blood vessel calcification and arteriosclerosis. When blood vessels begin to calcify and become narrow, it may lead to cardiovascular disease, myocardial infarction, arteriosclerosis, and stroke in the long run. These problems have nothing to do with supplementing high-calcium drinks or calcium tablets.
Vascular calcification may lead to cardiovascular disease crisis
When arteries accumulate too much calcium ions, blood vessels become calcified, causing many cardiovascular diseases. Depending on the location of vascular calcification, it can be divided into the following two types:
- Intimal calcification of arteries:
occurs in the intima of arteries and is mostly caused by inflammation. Calcification appears in irregular shapes. Obvious and clear calcified plaques can be seen in blood vessels, which is a typical precursor to arteriosclerosis. - Arterial medial calcification:
long strips of calcification, which mainly occur in the elderly, patients with diabetes, kidney disease, and uremia. Although this type does not affect the degree of stenosis of blood vessels, it will cause an increase in systolic blood pressure and a decrease in diastolic blood pressure, affecting heart function, and ultimately leading to symptoms of cardiovascular diseases such as myocardial ischemia, left ventricular hypertrophy, heart failure, and myocardial infarction.
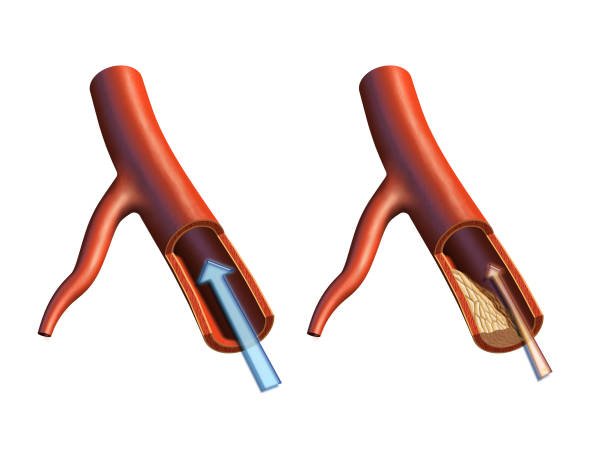
The vascular calcification index determines the severity of arteriosclerosis
Vascular calcification can be examined through LDCT low-dose computed tomography (low-dose lung computed tomography) to examine the location and degree of calcification. It can also predict the risk of cardiovascular disease. You can check whether you are facing cardiovascular disease according to the following vascular calcification index. Disease crisis:
- Calcium index 0: The risk of cardiovascular disease within 10 years is <1%.
- Calcium index 1~99: The risk of cardiovascular disease within 10 years is about 4%.
- Calcium index 100~399: The risk of cardiovascular disease within 10 years is about 13%.
- Calcium index >400: The risk of cardiovascular disease within 10 years is approximately 24%.
Who needs to undergo LDCT low-dose computed tomography? If you have the following risk factors, it is recommended that you go to a major hospital for examination:
- Hypertension
- Diabetes
- Hyperlipidemia
- Smoking, drinking
- Family history of cardiovascular disease
- High pressure working group
- Women over 55 or menopausal
- Obese people
The above-mentioned risk groups can undergo cardiovascular photography if necessary. If abnormalities are found, they can be treated early to avoid the risk of cardiovascular disease.
Can vascular calcification be reversed?
Unfortunately, there is no possibility of reversing vascular calcification, which means that once the problem of vascular calcification occurs, the blood vessels can never return to their previous state. For patients who have already developed vascular calcification, their living habits can be adjusted in the following ways:
- Control blood pressure and lower cholesterol
- Check for vascular calcification regularly
- Maintain a healthy weight
- Healthy diet
- Quit smoking and drinking













