What is Chelation Therapy? Can it Treat Heart Disease? Understand the Uses and Side Effects of Chelation Therapy
Chelation therapy, also known as chelation therapy, is mainly used to treat heavy metal poisoning. Based on its principles, some scholars have proposed that chelation agents can also be used to treat coronary heart disease and atherosclerosis. However, is this actually the case? This article will take you through it together.
What is chelation therapy?
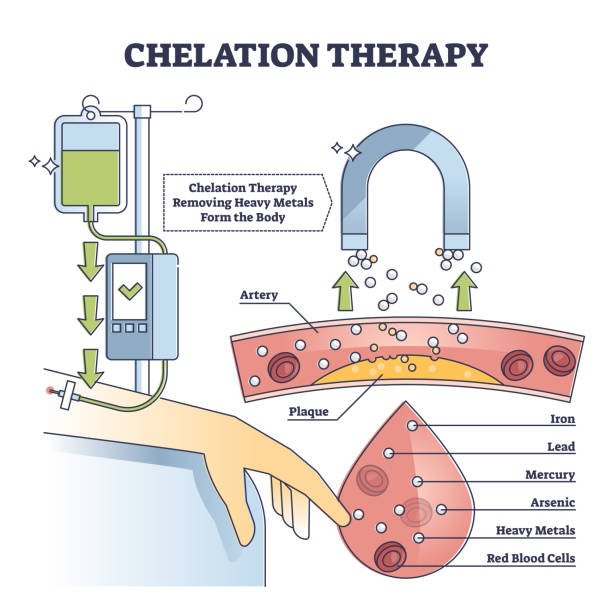
Chelation therapy is a drug called ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) (also known as chelating agent), which is injected into the patient’s body through intravenous injection. EDTA will combine with heavy metals in the blood and excrete heavy metals (mercury, lead, zinc, aluminum, etc.) through urine, reducing the harm of heavy metals to the human body.
Chelation therapy and cardiovascular disease
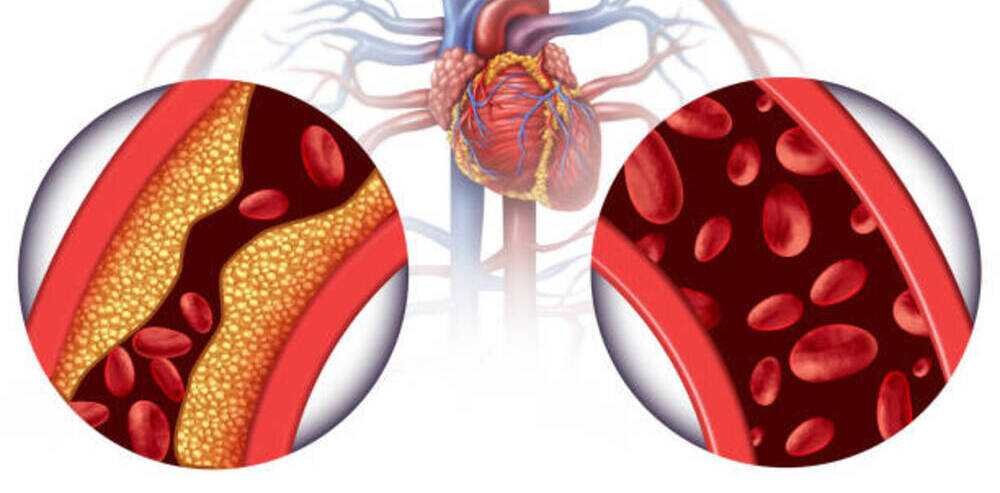
Coronary arteriosclerosis of the heart is associated with inflammation and oxidation of cholesterol. Cholesterol is mostly derived from saturated fat in food. After oxidation, many free radicals are produced, which release and oxidize the low-density lipoprotein (LDL, also known as bad cholesterol) in the cholesterol inside the arteries. Macrophages in white blood cells engulf oxidized bad cholesterol and form foam, which then adheres to the artery wall and gradually accumulates to form plaque. Plaque deposits on artery walls can narrow the arteries and damage them.
Seeing this, you may wonder what the connection between these fatty plaques is and chelation therapy? This has to talk about “calcium”. Since the human blood already contains calcium, atherosclerosis will make it easier for calcium in the human body to deposit there, causing “calcification.”
Although calcium is not classified as a heavy metal, it is still a metallic element. According to the principle of chelation therapy, EDTA can theoretically allow the agent to bind to calcium in arterial plaques. After the agent is combined with calcium, it will pass through the body circulation and urinary system with the blood flow, and finally be excreted from the body, thereby removing fatty plaque, The effect of unblocking blood vessels.

Does chelation therapy really treat cardiovascular disease?
For many years, chelation therapy has been used to treat lead poisoning and mercury poisoning. However, for cardiovascular diseases, the efficacy of chelation therapy is still unclear and controversial, and there is not enough evidence of effectiveness and safety to show that it can be used. as conventional therapy.
Therefore, authoritative heart disease organizations such as The American Heart Association and The American College of Cardiology are still unable to endorse chelation therapy, nor has the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Can be approved for implementation.
Today, chelation therapy is only FDA-approved to treat heavy metal poisoning, and there is insufficient evidence to support its use for any other condition. Due to concerns about side effects, it is recommended that patients fully discuss with a physician and expert before undergoing chelation therapy.
Side effects of chelation therapy
Chelating agents bind and remove some metals that the body needs, such as calcium, copper, and zinc, which can lead to deficiencies in these trace minerals and cause the following side effects:
Common side effects
- Burning sensation that patients may experience when receiving intravenous injections
- Headache
- fever
- feel sick and vomit
- Rare side effects
- Hypocalcemia
- heart failure
- kidney damage
- Bone marrow suppression