
My Heart Hurts So Much? Angina Pectoris = Angina! Chest Pain symptoms and Treatments
The heart is the most important blood-supplying organ in the human body. Abnormalities often cause significant discomfort to patients. Therefore, it is very important to have common sense to detect abnormal signs of the heart. Among the many symptoms, pain is often the most worrying and scary thing, especially what should you do if you feel pain in your heart or chest? Should I seek medical attention if I have chest pain? This article will take you through the symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment of angina pectoris.
What is angina?
Angina, also known as angina, refers to chest pain symptoms caused by blockage of the coronary arteries of the heart, resulting in a reduction in the amount of blood received by the myocardium. Therefore, angina often occurs in patients with coronary heart disease (also known as ischemic heart disease).
Symptoms of angina
Chest pain is one of the most common symptoms that patients feel, but it seems too abstract to rely solely on personal feelings. Most patients with angina say that their chests feel like they are being squeezed tightly or a heavy object is pressing on them, making them breathless. This may be used as a situational reference for identification. In addition, patients with angina may also have the following symptoms:
- Feel sick and vomit
- Difficulty breathing, rapid breathing
- Tired
- Dizziness
- Sweating
It is important to note that because women’s coronary microvessels are prone to blockage, their symptoms may not be as obvious as those of most men who have chest pain. However, female patients with angina are more likely to have the following atypical symptoms:
- Pain in the jaw, back, arms, and neck
- Stomach ache
- Pins and needles pain
- Difficulty breathing, rapid breathing
- Feel sick and vomit
- Indigestion
- Unusual fatigue
Types of angina
According to the different manifestations of angina pectoris, it can be divided into the following 3 types:
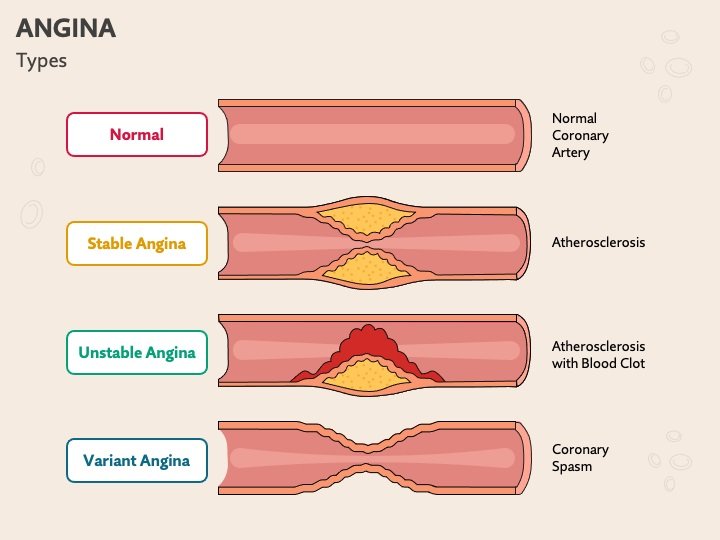
1.Stable angina
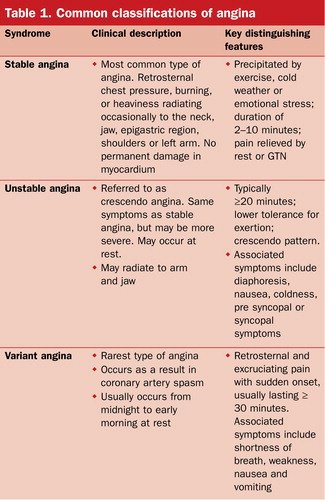
When engaging in exercise or physical training, because the heart requires more oxygen, narrowing of the arteries tends to restrict blood flow, which may cause stable angina. Some people may not have chest pain problems at ordinary times, but they are prone to angina as soon as they climb stairs or run. This is the reason. In addition, emotional stress, smoking, eating large meals or cold weather may also cause stable angina. The following are the characteristics of stable angina:
- Short duration (perhaps less than 5 minutes).
- Symptoms may be relieved with some rest or angina medication.
- It is more predictable when it will occur and is similar to previous symptoms of angina.
2.Unstable angina
Unstable angina is caused by the rupture of fatty plaques in the arteries, resulting in blood clots or thrombus, thus causing the diameter of the blood vessels to become very narrow, causing obvious symptoms of angina. This type is more dangerous than stable angina. If the reduced blood flow is not improved, complete blockage of the blood vessels will worsen into myocardial infarction. The following are the characteristics of unstable angina:
- It also occurs when resting
- Not relieved by rest or angina medications and gradually gets worse
- Usually longer in duration and intensity than stable angina (may exceed 30 minutes)
- unpredictable
3.Variant angina pectoris
Variant angina is a type of angina caused by coronary artery spasm, resulting in decreased blood flow. Therefore, it can also be called spasmodic angina. This symptom is quite rare and may be caused by cold weather, smoking, stress, vasoconstrictor drugs, drug use, etc. The following are the characteristics of variant angina:
- Symptoms are severe.
- It usually occurs at rest.
- It can be relieved by angina medications.
- The attack time is regular and usually occurs in the early morning or at night.
When should you seek medical attention for angina pectoris?
Having chest pain combined with the above symptoms does not necessarily mean that you have coronary heart disease. It still needs to be examined by a doctor to confirm. If you have frequent chest pain, it is recommended that you go to the hospital for examination. If chest pain often lasts for several minutes, even if you have rested or taken angina medicine, but the condition does not improve, please seek medical attention immediately. This is likely to be a precursor to myocardial infarction.
The difference between palpitations and angina pectoris
Many people often use “palpitations” to describe uncomfortable feelings in the chest or heart. However, palpitations actually mainly refer to changes in the heart beating frequency or intensity, causing the patient to feel uncomfortable or have a “pounding” feeling in the heart; while angina pectoris It means there is clear pain in the heart. It is important to note that palpitations may also be combined with an angina pectoris attack. Therefore, it is recommended that whenever you feel heart discomfort, you should seek medical treatment as soon as possible and receive a professional diagnosis from a physician.
Risk factors for angina
We already know that the main cause of angina is arterial narrowing, so any behavior that increases the accumulation of fat in blood vessels or causes damage to blood vessels will increase the chance of angina pectoris, such as:
- high cholesterol
- Triglycerides too high
- Hypertension
- Smokes
- Diabetes
- Women over 55 years old
- Men over 45 years old
- Family history of heart disease
- Lack of exercise
- Obesity
- Pressure
Diagnostic methods of angina
In addition to verbal consultation, doctors will use the following methods to check whether the patient has angina and distinguish its types to make appropriate medical treatment. There are several inspection methods:
- Electrocardiography
- Exercise electrocardiogram (Stress test)
- Echocardiography
- Chest X-ray
- Cardiac catheterization
- CT scan
- MRI (Cardiac MRI)

Treatment methods for angina
There are many treatments for angina, and depending on the severity of the condition, medications or surgery may be used. For the most common type of stable angina, the patient should rest in a sitting position and hold a Nitroglycerin tablet under the tongue. If the condition does not improve, please wait 5 minutes before taking another tablet. If the second tablet is taken, If the pain still persists after 5 minutes, seek medical attention immediately. Other treatments include:
1.Medical treatment
- Antiplatelet drugs: Such as aspirin or Clopidogrel, which can help the blood to clot less easily and reduce the incidence of blood clots.
- Cholesterol-lowering drugs: For example, statins, by blocking substances needed by the body to produce cholesterol, lower cholesterol concentrations and reduce blood vessel plaque blockage.
- Blood pressure lowering drugs: such as β-blockers, Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors (ACEI), and Calcium channel blockers (CCB). If a patient cannot use beta-blockers and CCBs, Ranolazine may be used as an alternative.
2.Surgical treatment
For patients who do not respond well to medication or lifestyle changes, doctors may use surgery to treat:
- Angioplasty: Also called balloon dilatation. Usually, a catheter is inserted from the patient’s femoral artery and guided to the blocked artery. The balloon is inflated to open the blood vessel and increase blood flow. Depending on the situation, the doctor may decide whether to insert a stent to prevent the blood vessel from becoming narrowed again.
- Coronary artery bypass surgery: If angina is caused by stenosis of multiple coronary arteries, this surgery may require the transplantation of blood vessels from elsewhere to replace the severely blocked coronary arteries.
- Enhanced external counterpulsation (EECP): By tying compression bands on the legs and buttocks, the air bags will inflate to apply pressure when the heart relaxes; when the heart contracts, they will deflate and relax, allowing the heart’s coronary arteries to relax. Increased blood flow.
Prevention methods of angina
The following methods can not only prevent angina, but if you already have angina, these methods can also help you improve your symptoms:
- Quit smoking.
- Don’t drink excessively.
- Relieve stress at the right time.
- Measure regularly to know whether your cholesterol and blood pressure index are normal.
- Maintain a moderate weight but not overweight.
- Eat a healthy diet (less saturated fat).
- If you have no history of angina or heart disease, you should increase the frequency of exercise; if you have a regular exercise habit, it is recommended to consult a doctor to choose an exercise method that suits you.












