Is a Fast Heartbeat a Palpitation? How to Deal With it? Need to See a Doctor? Reason For Too Fast?
Fast heartbeat is a very subjective feeling. Some people feel that their heartbeat is too fast, but after actual testing, it is normal; some people may have a heartbeat that is too fast without knowing it. If the heartbeat is often too fast, in addition to fainting, night sweats, and weakness, it may even be fatal in severe cases.
In this article, we explain to you the definition of a fast heartbeat and teach you how to identify a normal heartbeat? It also explains the causes, types and symptoms of tachycardia, and tells you which department should be checked for tachycardia.
What is the normal heartbeat value? What is the definition of fast heartbeat?
Under normal circumstances, if an adult is stationary, the heartbeat rate is about 60 to 100 beats per minute. If your heartbeat frequently exceeds 100 beats without engaging in any activity, you may have tachycardia, which means your heartbeat is too fast.
The best way to judge whether your heartbeat is too fast is to count your heartbeat with a blood pressure monitor or pulse when you feel palpitations or irregular heartbeat, and write down the number of heartbeats. If it often exceeds 100 or even 140 beats, please seek medical advice as soon as possible. Further cardiac testing.
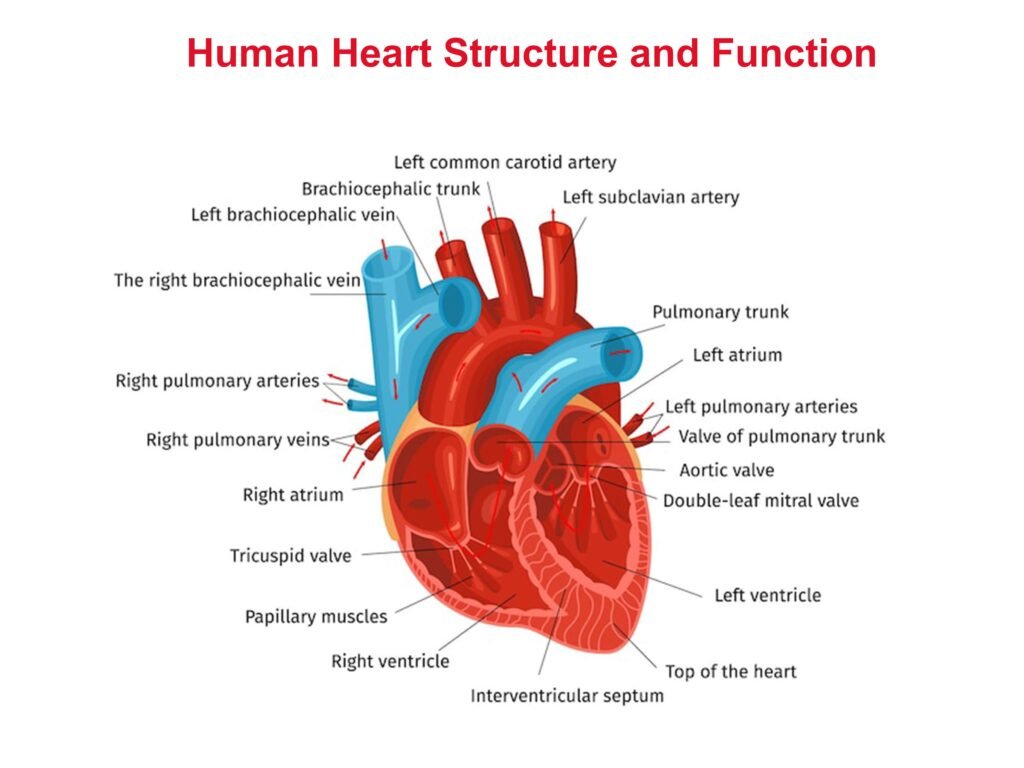
What happens if your heart beats too fast? Looking at physical health from the heartbeat
A normal heartbeat begins in the right atrium, discharges from the sinoatrial node, stimulates the beating of the right atrium and left atrium, and flows blood to the left and right ventricles. When the electrical signal is sent to the atrioventricular node in the middle of the heart, the signal is split into two and sent to the left and right ventricles to make them beat and contract. Then the blood is sent to all parts of the body to provide nutrients and exchange gases.
It can be seen that the heartbeat is an important part of the human body’s circulatory system; if the heartbeat is too fast, too slow, or abnormal, it will affect the blood output of the heart, hinder the normal operation of the body, and thus endanger health.
Causes and types of fast heartbeat
Clinically, a fast heartbeat is usually caused by a problem with the atria or ventricles of the heart. The most common atrial abnormality is atrial fibrillation, while the most common ventricular abnormality is paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia.
- Atrial fibrillation
- Atrial flutter
- Atrial tachycardia
- Supraventricular tachycardia
- WPW syndrome (Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome)
- Ventricular pulsation (also known as ventricular tachycardia)
- Sinus tachycardia
- Long QT syndrome

Fear of heart palpitations and chest tightness due to fast heartbeat
Palpitations are symptoms of a fast heartbeat. In addition to palpitations, chest tightness, or dizziness, a fast heartbeat may also cause the heart to beat too fast for a long time, reduce atrial activity, cause atrial blood to coagulate, form blood clots, and flow to the brain, causing a stroke.
Compared with those with a normal heartbeat, patients with atrial fibrillation are five times more likely to have a stroke. Severely fast heartbeats may also lead to shock or even sudden death. Therefore, if you find that your heartbeat is often too fast, it is recommended to seek medical treatment as soon as possible to find out the cause and receive treatment.
Common symptoms of a fast heartbeat include:
- Palpitations
- Chest tightness, chest pain
- Dizziness
- Burnout
- Respiratory asthma
- Night sweats
- Difficulty breathing
- Hypotension
- Weak and feeble
- Cold hands and feet
- Unconsciousness, fainting
How to deal with a fast heartbeat? Need to see a doctor? Which subject should I look at?
If you have frequent heart palpitations or shortness of breath, and your own heartbeat often exceeds 100 beats, it is recommended that you go to the cardiology clinic of the hospital for examination. If there is only occasional tachycardia, you can observe the occurrence of tachycardia, for example:
- Does your heart beat too fast at certain times?
- Does your heart beat too fast after engaging in certain activities?
- Does your heart beat too fast after eating or taking certain foods or medications?
If the cause is found, please reduce the conditions that may cause tachycardia, maintain adequate rest and sleep, keep your mood calm, and limit exposure to irritating substances such as tobacco, alcohol, or caffeine to maintain heart health.
If your heartbeat suddenly becomes too fast and you experience fainting, weakness or difficulty breathing, please sit down or lie down immediately and seek medical treatment as soon as possible.












