Understanding Cervical Cancer: 90% of Patients Have Been Infected with HPV – Cervical Cancer Symptoms, Treatment, Risks and Survival Rates
Cervical cancer is a cancer that occurs in the cervix. More than 90% of cervical cancers are caused by abnormal cell growth caused by HPV virus infection, and then evolve into cancer. Cervical cancer is one of the common cancers in women. Women of all ages may suffer from cervical cancer. cervical cancer, which is found anywhere in the cervix (the opening between the vagina and the womb).
The cervix is located at the opening from the lower half of the uterus to the vagina. Because it is the narrower part of the uterus, it is called the “neck.” The opening of the cervix leads to the vagina and is also the passage for menstrual flow, as well as vaginal microorganisms and air. Barrier to the female uterus. If you look inside the vagina, the cervix looks like a round protrusion with an opening in the middle. During sexual intercourse, the cervix can also resist inflammation caused by stimulation.
Cervical cancer symptoms
Symptoms of cervical cancer are usually not obvious until invasive cervical cancer develops before symptoms begin. To detect it early, you must rely on tests such as Pap smear screening. Common symptoms of cervical cancer are as follows:
- Increased leucorrhea
- Leucorrhea is clearer and thinner
- Leucorrhea with peculiar smell
- Vaginal discharge has a peculiar smell
- Vaginal bleeding after sex
- Vaginal bleeding after strenuous labor
- Vaginal bleeding after genital examination
- Vaginal bleeding in menopausal women
If you already feel pain in your body, you may have symptoms of more advanced cervical cancer:
- Feeling uncomfortable after sex
- Sciatica
- Lower abdominal pain
- Back pain
- Hydronephrosis
- Incontinence
- Bleeding in urine and stool
- Weight loss
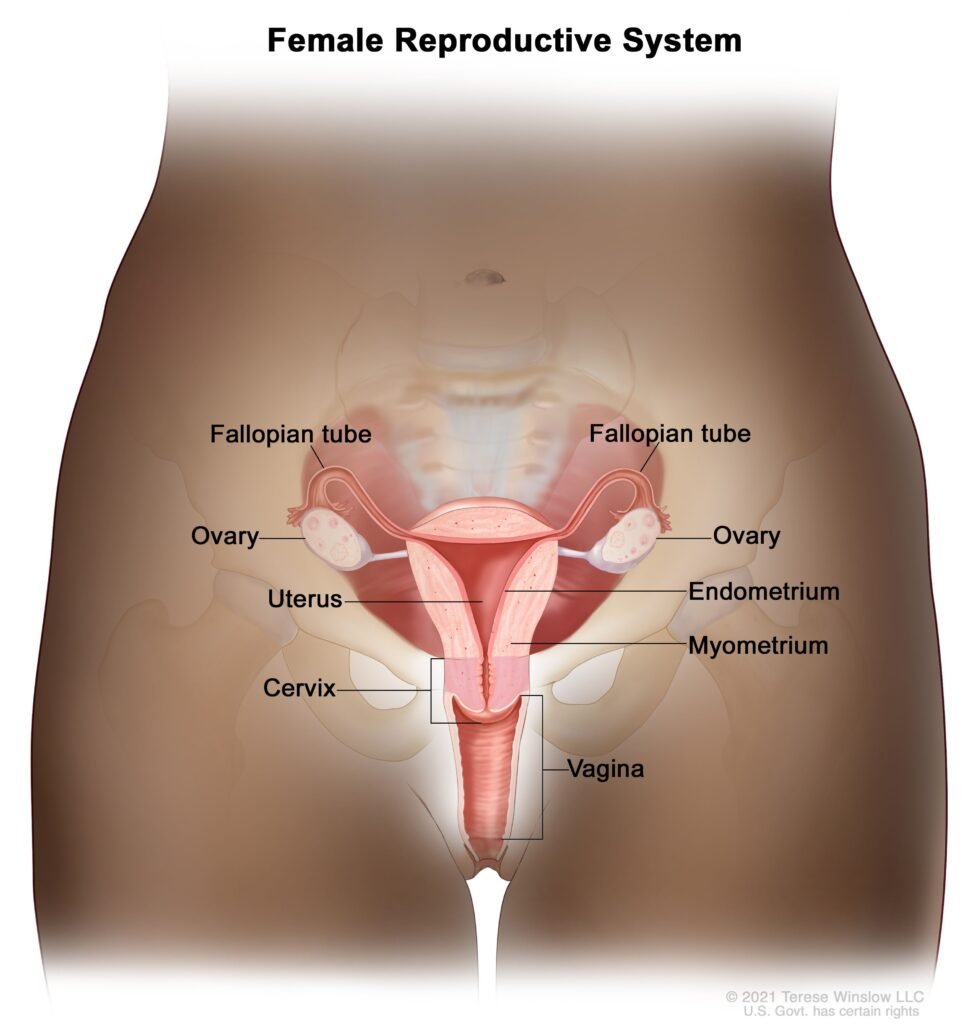
Cervical cancer causes, risks and prevention
Causes of cervical cancer
The main cause of cervical cancer is infection with the Human Papillomavirus (HPV) through sexual intercourse, which causes cells to proliferate abnormally and transform into cervical cancer cells. When cervical cancer occurs, the early stage of cervical cancer will first appear. The lesion is called Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia.
Cervical Cancer Risk
More than 90% of cervical cancer patients have been infected with HPV, but most infected people will not develop cancer. Other risks of cervical cancer include the following behaviors:
- Have sex earlier
- Having multiple sexual partners
- Sexual partners themselves also have multiple sexual partners
- Sexually transmitted infections
- Cervical cancer is most likely to occur between the ages of 35 and 45
- Long-term damage, skin rupture, and inflammation of the cervix
- Smoking

Cervical Cancer Prevention
The 5-year survival rate of early-stage cervical cancer is as high as over 90%. Therefore, the National Health Service of the reminds you that there are three lines of defense that you must pay attention to in preventing cervical cancer:
- Safe sex
- Get HPV vaccine
- Get regular Pap smears
Cervical cancer staging
The International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics (FIO) divergent system is the most commonly used staging system for cancers of the female reproductive system. Cervical cancer can be divided into 5 stages:
- Cervical Cancer Stage 0
- Cervical Cancer Stage 1
- Cervical Cancer Stage 2
- Cervical Cancer Stage 3
- Cervical Cancer Stage 4
Classification of cervical cancer
Cervical cancer categories include:
- Squamous cell carcinoma
- Adenocarcinoma
- Adenosquamous carcinoma
- Clear cell carcinoma
- Endometrioid adenocarcinoma
- Undifferentiated carcinoma
- Neuroendocrine tumors include small cell carcinoma
Diagnosis of cervical cancer
Since the early symptoms of cervical cancer are not obvious and everyone’s symptoms are different, early diagnosis and examination are very important. Depending on the condition of the cancer cells, doctors will provide different detection methods. Listed below are the 6 diagnostic categories of cervical cancer:
- Pap smear test
- Pelvic exam
- Colposcopy
- Cone resection
- Dilation and curettage
- Urine test, blood test, X-ray, etc.

Cervical Cancer Treatment
- Operation
- Radiation Therapy
- Chemotherapy
- Targeted drug therapy
- Peace and Palliative Care
Recurrence of cervical cancer
The so-called 5-year survival rate is also a reference indicator used by doctors to predict a patient’s condition. Each case is different. Factors to be considered include the gene activity of the cancer cells and the patient’s treatment status. Here are three possibilities for cancer cells to come back:
- In situ tumor
- Local metastatic tumor
- Distant metastasis
In addition to local invasion and spread, cervical cancer can also easily metastasize to adjacent lymph glands and distant sites through the lymphatic system. Generally speaking, the prognosis for patients with intrapelvic or paraaortic lymph gland metastasis is probably not optimistic.
Average five-year survival rate for cervical cancer
- Cervical cancer stage 1: 100%
- Cervical cancer stage 2: 60~90%
- Cervical cancer stage 3: 20~60%
- Cervical cancer stage 4: <20%