What is Glycemic Load? Relation of GI and GL
What is glycemic load? What is its relationship with the glycemic index? Maybe I have been eating so-called low GI foods (such as sweet potatoes, whole-wheat bread), but the weight control people still gain weight, and the blood sugar control of diabetics are not relatively stable. What is the problem? In fact, it is caused by not noticing the hidden key factors!
What is the GI value we often hear?
The full name of GI value in English is Glycemic Index. What it means is that when a certain food is eaten into the stomach, the blood sugar level in the blood will rise after digestion.
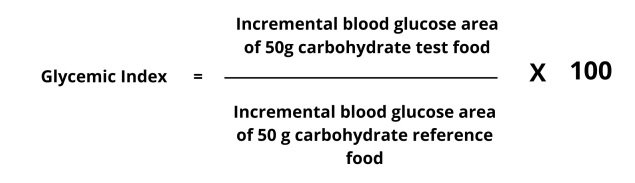
When eating food with a higher GI value, the blood sugar level will increase after eating. The rise is higher, and simultaneously, the pancreas will secrete insulin to lower the blood sugar level. By sending sugar into various cells of the body, it will balance the blood sugar level in the blood, and this will cause two results:
Results 1) The blood sugar rises rapidly, and also falls quickly. You may get hungry again soon.
Result 2) When there is too much sugar, insulin is a synthetic hormone that will cause it to become fat and store it in fat cells, which will lead to the often heard risk of poor blood sugar control or getting fatter.
Emphasizing GI value is insufficient, actually there is a hidden deficiency.
If you have been eating a lot of low GI foods, wouldn’t the accumulated amount cause your blood sugar to rise even higher?
The answer is yes! So that is why some people have been eating low GI foods and may still not achieve the desired results, because the hidden lack of GI value is the lack of “quantity” control.
Understanding GL value: glycemic load
Therefore, GL value glycemic load is the total result of “food + quantity size”, which can also tell whether the food you eat is excessive.
The calculation formula is: glycemic load = (glycemic index value x carbohydrate content per serving) ÷ 100
If the calculated GL value is
< 10, it is called “low glycemic load”,
10 – 20 is “moderate glycemic load”,
>20 or more is a “high glycemic load”.
The amount you eat will affect your glycemic load
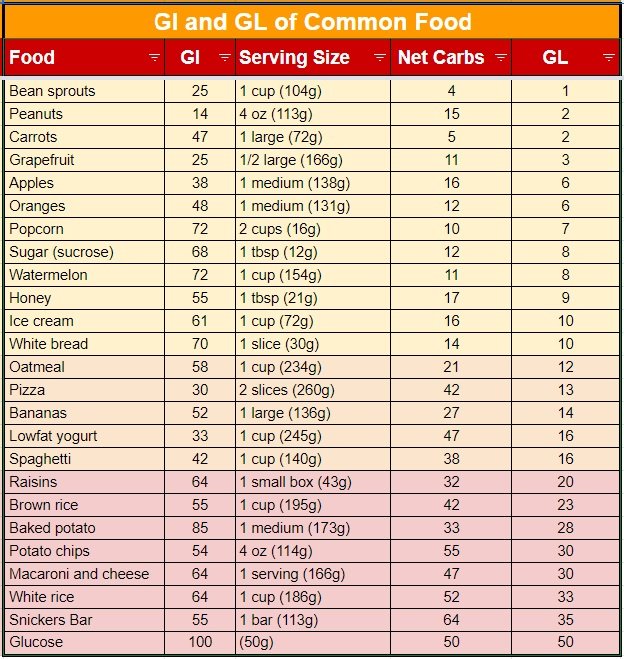
If you take watermelon as an example, the GI value of watermelon is as high as 72. It is a food that can easily cause blood sugar to rise rapidly after two hours. However, if you only eat a piece of watermelon (about 150 grams), the GL value is 4. Belongs to low glycemic burden. So this result shows that as long as the amount of food eaten is moderately controlled, and if the watermelon juice is not drunk or excessive watermelon is eaten, watermelon can be considered low-risk food.

Nutritionists suggested that both GI and GL need to be considered together for any food recommendation, because the glycemic index is to consider the quality of food, and the glycemic load is to consider the amount of food. When eating, it is better to consider both quality and quantity. At the same time, it can also maintain stable blood sugar and health.
Glycemic Index (GI) & Glycemic Load (GL) Guide
Book Recommendation:
Buy “GI & GL Counter” online
Buy “Glycemic Index & Clycemic Load of Foods” online
Recommended Supplement For Diabetes
-
1. Promote methyl transfer
2. Promote the development and maturation of red blood cells, keep the body’s hematopoietic function in a normal state, prevent pernicious anemia; maintain the health of the nervous system
3. In the form of coenzyme, it can increase the utilization rate of folic acid and promote the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats and proteins
4. It has the function of activating amino acids and promotes the biosynthesis of nucleic acids, which can promote the synthesis of proteins, which plays an important role in the growth and development of infants and young children.
5. Metabolize fatty acids so that fats, carbohydrates, and proteins are properly used by the body
6. Eliminate irritability, concentrate, enhance memory and balance
7. It is an indispensable vitamin for the healthy functioning of the nervous system and participates in the formation of a lipoprotein in the nervous tissue
-
Benefit of Beef Gelatin
- Collagen and gelatin contribute to the infrastructure of connective tissue throughout. Regular consumption of these proteins helps repair and care for the intestines, skin, hair, tendons, cartilage, bones and joints.
- Supports joint health, comfort and mobility.
- Supports gut health and digestion due to the role of amino acids in promoting the integrity of the gut lining
- Boost muscle mass
- Reduce hunger
- Supports bone health
- Assist with blood sugar control
- Supports cognitive functions, including memory and learning
- Helps Athletic Performance and Recovery
- Helps maintain healthy, youthful skin
- Promotes healthy hair and strong nails
- Promote quality sleep





































