
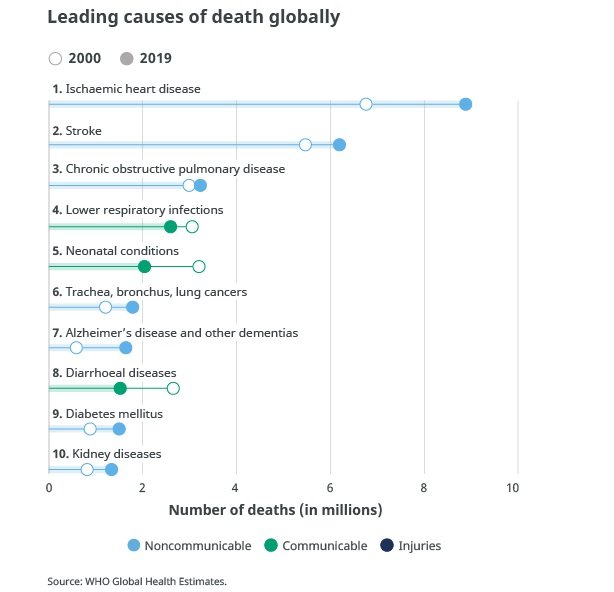
Diabetes! One of the top ten causes of death in the world
Diabetes has always been one of the top ten causes of death in the world. Many complications accompany diabetes, such as kidney disease, retinopathy, peripheral nerve decline, and cardiovascular disease. Poor blood circulation may also lead to poor wound healing and even amputation. And glycosylated hemoglobin is one of the indicators for diabetes detection. Next, let a nutritionist guide you to understand what glycosylated hemoglobin is, the difference between “glycation” and “glycosylation“, the relationship with fasting blood sugar, and how to improve it by habit if it is too high.
Heme is the protein on the surface of red blood cells that carries oxygen around the body and removes carbon dioxide. When glucose enters the blood and combines with hemoglobin to form glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1C); glucose can attach to hemoglobin until the hemoglobin is destroyed. The lifespan of hemoglobin is about 2-3 months. So we can use the average glucose concentration in the past to deduce the glycosylated hemoglobin. However, glycosylated hemoglobin is not the only indicator, and it needs to be evaluated together with fasting and postprandial blood sugar. In 2016, the official journal of “The Gerontological Society of America” (The Gerontological Society of America) found that the concentration of glycosylated hemoglobin was related to the rate of decline in physical function.
General health checkups and clinical checkups include glycated hemoglobin testing, and an excessively high HbA1C index is associated with many chronic diseases (such as diabetes, cardiovascular disease). Generally, the detection value of HbA1c falls between 4-5.6%, and the value of 5.7-6.4% is a high risk of diabetes. For example, if the test value of HbA1c is 6, it belongs to the stage of pre-diabetes, and it is likely that the normal value can be restored by adjusting the daily diet and living habits. Diabetes is already diagnosed when the value is higher than 6.5%, and you must follow the instructions of a professional doctor to take medicine and adjust your diet to change. When the value is lower than 7%, it is still in the range that can effectively prevent chronic complications of diabetes. However, when the value is higher than 8%, it means blood sugar is not well controlled, and you should seek medical attention as soon as possible.
What is the difference between “glycation” and “glycosylation” hemoglobin?
The biggest difference between “glycation” and “glycosylation” is whether there is “enzyme” involved! There are two kinds of glycosylation in our body. One is the enzymes to bind sugars to specific positions on proteins, and its molecules will have special functions, that is, “glycosylation”; the other “glycation”, also known as “non-enzymatic glycosylation” is the combination of excessive sugars with proteins or lipids without the action of enzymes. At this time, the proteins and lipids will mutate, and finally “Glycation end products” (AEGs) will be produced. “Glycation end products” (AEGs) will increase blood sugar, and the state of high blood sugar will easily cause the cells of the whole body to be in a state of chronic inflammation. In addition to diabetes, chronic kidney disease, Alzheimer’s disease, cardiovascular disease, etc. Chronic diseases are all related to glycation. “Glycated hemoglobin” is glycation without the action of enzymes, using this method to know the content of glucose in the blood.
According to the Diabetes Medical Calculation, glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1C) can also be used to convert the average blood sugar in the past 3 months. The formula is as follows:
Average blood sugar level in the past 3 months (mmol/L) = 10.929 * (A1C(%) – 2.15)
For example, when the glycated hemoglobin (HbA1C) is 5.9%, the average blood sugar level in the past 3 months is about: 10.929 x (A1c(%)-2.15) = 10.929 x (5.9-2.15) = 41
We can also directly use the test results of glycated hemoglobin (HbA1C) to assess whether it is too high
Diabetic patients have to monitor both the glycated hemoglobin and blood sugar?
After all, glycated hemoglobin is to observe the average blood sugar of the human body in the past 3 months. Even if you know the HbA1c, you still need to observe the blood sugar, especially the daily life schedule is slightly different, such as daily diet, exercise and even medication habits. Both may affect daily changes in blood sugar. Therefore, nutritionists suggest that both glycated hemoglobin and blood sugar indicators should be checked, especially for diabetics!
For diabetes, is lower A1C = better health?
Studies have found that if you maintain low glycated hemoglobin for a long time, you may still experience physical dysfunction, and the probability increases by 25% every year! Therefore, it is recommended to maintain the glycated hemoglobin at 4.5%-6% in order to maintain long-term health.
What should I do if I have high glycated hemoglobin?
Improve your habits as follows:
-
- Maintain exercise habits
Muscle contraction during exercise consumes a lot of blood sugar, and at the same time can adjust blood pressure and strengthen cardiovascular function. In addition, it can also exercise the sensitivity of insulin secretion. Maintaining exercise habits can be said to be the most effective way to reduce glycated hemoglobin and treat diabetes! Nutritionists recommend that you spend some time every week doing aerobic exercises such as jogging, climbing, or brisk walking. - Improve diet
Choose low-sugar foods. Carbohydrates include sugar and starch foods, which will be converted into glucose and raise blood sugar. Refined starches such as white rice and starchy processed foods such as pasta, bread, etc. can be converted to whole grains such as brown rice or oats. High-salt, high-sugar seasonings, delicate pastries, high-cholesterol foods, and high-GI foods should all be avoided. Simply to say, all the foods that cause blood sugar to spike suddenly should be avoided. The order of eating is also very important, according to: Vegetables > Protein (Meat) > Carbohydrate (low carb) > Soup > Fruits can slow down the rate of blood sugar rise. The body mainly controls blood sugar through the secretion of insulin, so the most important thing to reduce glycated hemoglobin is to maintain the balance of blood sugar and avoid excessive intake of sugar! - Reduce weight
Many studies have shown that weight loss can improve many physical conditions, but nutritionists emphasize natural weight loss methods and try not to use drugs to control them, because weight loss drugs may cause more serious side effects. Studies have also shown that losing 5-10% of your original body weight can reduce your risk of diabetes by 58%. - Foot care
Diabetic foot is a very common complication of diabetes. Severe cases may lead to hospitalization or even amputation. Therefore, it is necessary to pay attention to the cleaning of feet, toenails and the safety of feet during exercise to avoid wounds. - Other complications
Diabetes will affect the condition of the whole body, so you should always pay attention to whether there are other diseases in your body. You should always go to the hospital regularly to measure blood pressure, check teeth, eyesight, protein in urine, triglycerides, etc. Pay attention to the complications, such as retinopathy, diabetes foot, heart attack, stroke, nephropathy, neuropathy, gum disease, and related conditions like cancer.
- Maintain exercise habits
In general, the assessment of whether you have diabetes must refer to the glycated hemoglobin and the blood sugar levels before and after meals. After eating, the food is digested and absorbed, and glucose enters the blood. When the blood sugar level rises, it will stimulate the secretion of a large amount of insulin to reduce the high blood sugar after meals. Diabetes means that the secretion of insulin is abnormal, and it is always in a state of high blood sugar. “Glycated hemoglobin” represents the average blood sugar in the past three months, and “fasting blood sugar level” represents the pancreas’ ability to maintain normal insulin levels.
Then how to see the blood sugar status of the body from glycated hemoglobin, blood sugar before meals (fasting blood sugar) and blood sugar after meals? The nutritionist sorted out the three in a table:
| HbA1c | Sugar Level Before Meal | Sugar Level After Meal | |
| Normal Value | 4.0~5.6% | < 5.6 mmol/L | < 7.8 mmol/L |
| Pre-diabetes | 5.7~6.4% | 5.6~7.0 mmol/L | 7.8~11.1 mmol/L |
| Diabetes | >6.5% | >7 mmol/L | >11.1 mmol/L |
Finally, if there are abnormalities in glycated hemoglobin, fasting blood sugar, and postprandial blood sugar, it is recommended to consult a professional medical professional to assess whether you are at risk of diabetes.
In addition, if you want to prevent diabetes, bitter gourd peptide, a popular health food in recent years, can be proven to lower glycated hemoglobin and fasting blood sugar, and has the effect of regulating blood sugar metabolism. It is a new type of health product that promotes metabolism.














