What is normal blood sugar two hours after a meal?
The 58-year-old Auntie Nancy was diagnosed with diabetes last year. Under the doctor’s advice, Auntie Nancy also measured blood sugar regularly in addition to taking medicine every day. Sometimes 11.5mmol/L, sometimes 8.5mmol/L, Auntie Nancy did not feel uncomfortable, which made Auntie Nancy very confused, so she came to consult her doctor and asked, ” What is the normal blood sugar two hours after meals?”
Postprandial blood glucose represents the blood glucose level after a glucose load and is generally measured 2 hours after breakfast. Postprandial blood sugar is very important for diabetic patients. People spend most of the day in the postprandial blood sugar state. The quality of postprandial blood sugar control directly reflects the quality of diabetes control. Some studies have found that postprandial blood sugar is closely related to complications such as macrovascular, microvascular, and kidney complications of diabetes. The higher the postprandial blood sugar, the greater the possibility of complications.
Postprandial blood glucose should be calculated from the first meal. Normal blood glucose should not exceed 10.0 mmol/L (180 mg/dL) half an hour after a meal and 1 hour after a meal; 2 hours after a meal, blood glucose should not exceed 7.8 mmol/L (140 mg/dL), roughly in the range of 3.3 to 7.8 mmol/L (60 to 140 mg/dL); when the 2-hour postprandial blood glucose is 7.8 to 11.1 mmol/L, it can be diagnosed as impaired or impaired glucose tolerance; when When postprandial blood glucose exceeds 11.1 mmol/L, it indicates diabetes, which can cause various complications, such as kidney disease and macrovascular disease.
For normal people, if the blood sugar is higher than 7.8 mmol/L 2 hours after a meal, it is not normal, and it is recommended to further check to confirm whether there is impaired glucose tolerance; for patients who already have diabetes, The conventional target of blood glucose control two hours after meals is <10.0mmol/L, and the strict target is <7.8mmol/L. This strict target is often for newly diagnosed, short course, young age, no diabetic complications and serious concomitant diseases. Type 2 diabetes patients.
In addition, different physical conditions often require different requirements:
For patients with mild disease course, good physical condition, and low blood sugar, the best postprandial blood sugar should be controlled within the range of 5.5~7.8mmol/L, and the worst should not exceed 8mmol/L;
Patients with a long course of disease, old age, prone to hypoglycemia, and multiple diseases can relax a bit, try to control it within 10.0mmol/L, and the worst can not exceed 11.1mmol/L;
For some special groups, gestational diabetes patients, high blood sugar can cause fetal malformation, premature birth, stillbirth and other problems. It is necessary to strictly control the postprandial blood sugar, and it is best to control the blood sugar below 6.7mmol/L 2 hours after the meal.
It can be clearly seen from the data that Auntie Nancy’s postprandial blood sugar control is still not ideal. The data shows that only 22.7% of patients with type 2 diabetes have achieved the standard of postprandial blood sugar management. If you want to better control postprandial blood sugar, pay attention to four tips
- Eat a reasonable diet
Diet directly affects postprandial blood sugar. The Chinese population is characterized by high carbohydrates, which is more likely to lead to increased postprandial blood sugar. Therefore, we should pay attention to the diet, strictly control the intake of carbohydrates, allocate the total amount of the day, the food structure should be reasonable, the variety should be as rich as possible, and the thickness, meat and vegetables should be reasonably matched. It is recommended that diabetic patients take the order of drinking soup first, then eating vegetables, and finally eating meat and staple food. - Proper exercise
Exercise has always been an important means to assist in lowering blood sugar. Appropriate exercise about half an hour after a meal can help reduce the blood sugar level two hours after a meal. Be careful not to exercise too vigorously. - Choose the right medicine
The disease conditions of diabetic patients are often different. Some people have high fasting blood sugar, while some people have high postprandial blood sugar. For those with poor postprandial blood sugar control, it is recommended to choose drugs that specifically target postprandial blood sugar, such as Ruixue , Miglitol tablets, which are α-glucosidase inhibitors, can reduce postprandial blood sugar by delaying the absorption of carbohydrates. - Regularly monitor postprandial blood sugar
The quality of blood sugar control cannot be based on feeling. Many people often have no discomfort even if their blood sugar is very high. Therefore, daily blood sugar monitoring must be done. When monitoring, not only fasting blood sugar, but also postprandial blood sugar, if abnormal , and adjust the treatment plan in time.
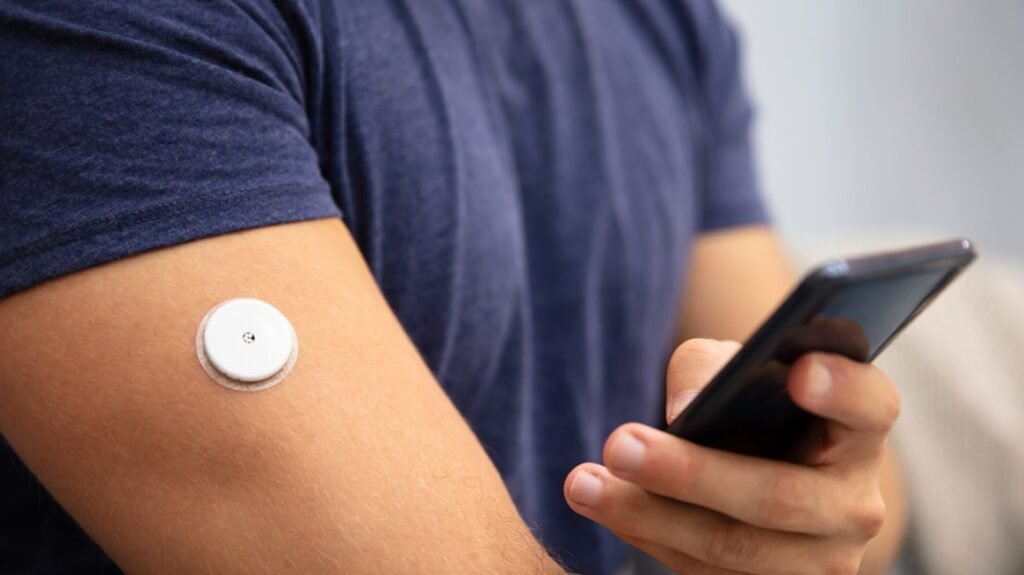
To closely monitor the blood sugar level throughout the day Abbott FreeStyle Libre 2 Sensor is the best device to monitor your blood sugar level. With this device you will know which food will spike your blood sugar
If affordable, I strongly recommend using FreeStyle Libre sensor, which no longer needs finger-prick. Painless 1-second scan to monitor your glucose throughout the day. You just scan the sensor as many times as you like throughout the day. Also, you can write down the food and quantity you take after each meal. Most important of all, it displays a continuous graphic report to show you the up and down of sugar level. All the data generated will automatically be sent to your doctor. If you have sufficient data for over 3 months, the A1C index will display.













