Just Because There’s No Sun Doesn’t Mean You Don’t Need Sunscreen! Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma Causes, Characteristics and Treatment
As the epidemic slows down and vaccinations become more popular, many people have begun to resume daily outdoor activities and go out of their homes to connect with nature again. However, no matter the season, while enjoying the sunshine and absorbing vitamin D, ultraviolet rays are also quietly attacking If your skin is exposed to the sun for too long, moles and melanin will develop, which may lead to a significant increase in the chance of skin cancer! Even if you go out on cloudy and rainy days when you can’t see the sun, 90% of ultraviolet rays can penetrate the insulating clouds and cause damage to the skin such as photoaging and cell cancer. Therefore, even if there is no sun, it does not mean that you do not need sun protection. We will take you to learn more about the causes, characteristics, and related treatment and detection methods of “Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC)”, one of the three major skin cancers.
What is cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma?
Squamous cell carcinoma, also known as squamous cell epithelioma, is generally less understood than melanoma, which has a higher fatality rate and is better known.
This squamous is not that squamous
Some attentive readers may have discovered, “Isn’t squamous cell carcinoma a type of squamous cell lung cancer?”
Yes, squamous cell carcinoma is caused by squamous cell lesions turning into cancer cells. In addition to the skin, it may also occur in the lungs, thyroid, esophagus or vagina, so even if it is squamous cell carcinoma, it may also refer to It’s a completely different type of cancer!

Easily evolves from solar keratosis
Just like other skin cancers, overexposure to ultraviolet rays is the main cause of squamous cell carcinoma. Therefore, the arms, face, lips, ears, and calves, which are areas prone to sun exposure, are all prone to squamous cell carcinoma. .
However, squamous cell carcinoma actually has a predecessor, which is Actinic keratosis (also known as actinic keratosis), which is also caused by frequent sun exposure. Actinic keratosis looks like a thick layer of hard skin and scabs, with a brown or red color. There may also be peeling. Patients may regard it as age spots and delay treatment, causing them to develop into scales. shape cell carcinoma.
More common in the elderly
Cell lesions caused by ultraviolet radiation do not occur overnight, and symptoms often appear only in old age. In particular, working farmers are at a relatively high risk of suffering from squamous cell carcinoma. It is recommended that they pay attention to whether there are any unknown moles or patches on their bodies for signs of skin cancer, and go to the hospital for examination as soon as possible to prevent cancer.
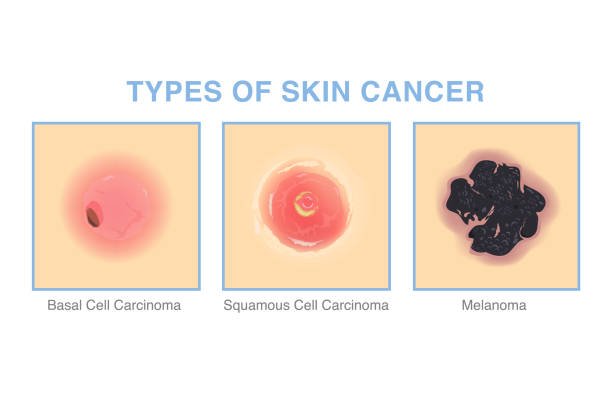
Characteristics of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma
The appearance of squamous cell carcinoma looks more like a scab. Because the lesions are prone to ulceration, they often appear red or flesh-colored. However, if there is no bleeding, they may appear as brown raised scabs. Unlike other skin cancers, squamous cell carcinoma lesions tend to grow very large and appear to be visibly raised like small red bumps.
Other risk factors for cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma
Ultraviolet solar radiation is the most common cause of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma and is a major risk factor for cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma; long-term exposure to carcinogens (such as tar in cigarettes) can also lead to the development of squamous cell carcinoma. Other possible causes include severe burn scars, years of ulcers, people undergoing organ transplants who take medications to suppress their immune response, and certain types of human papillomavirus (HPV) and AIDS, particularly in the genital area. The patients are all at high risk of suffering from squamous cell carcinoma.
In addition, genetic diseases such as Xeroderma pigmentosum, Albinism and Actinic keratosis are risk factors that people with a family history of this disease should not take lightly. Since the p53 protein has the function of preventing the replication of cells with mutated or damaged DNA, if the P53 gene is mutated, the p53 protein will lose its function, and cells with damaged DNA (such as squamous cell carcinoma) will become able to replicate.
As mentioned before, ultraviolet rays can easily cause squamous cell cancer. Therefore, the less melanin in the skin, the less resistant it is to ultraviolet rays. Therefore, compared with Asians, Caucasians are not only more susceptible to squamous cell cancer. , as well as other types of skin cancer. Having said that, being Asian should not be taken lightly; other risk factors include long-term wound healing, chronic arsenic poisoning, or the use of certain drugs such as immunosuppressants, which all increase the risk of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma.
We mentioned earlier the importance of early treatment. Using the ABCDE test to observe whether there are any abnormalities in moles or plaques on your body is very helpful for early treatment. The key points are as follows:
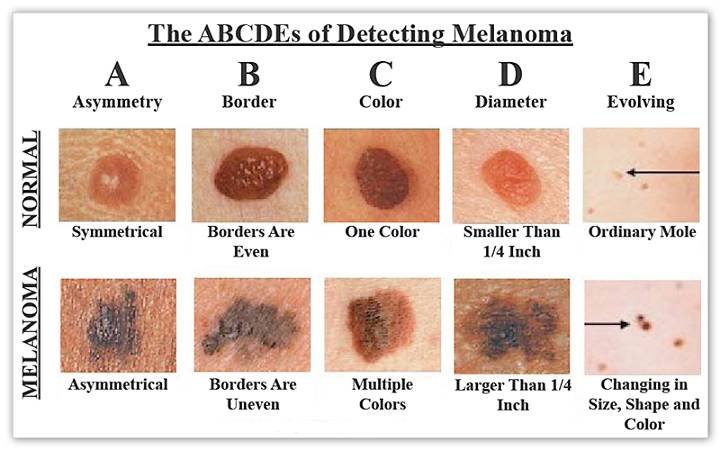
Diagnosis of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma
The diagnosis of squamous cell carcinoma is similar to that of other skin cancers. At the beginning, the doctor will make a preliminary diagnosis through physical examination. If the doctor suspects the possibility of skin cancer, he will further perform a biopsy and observe the examination through a microscope. body to determine the type and stage of skin cancer. Imaging tests, such as computed tomography (CT), X-ray, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), etc., may also be used depending on the situation.