What Causes Ovarian Cancer? Self-examination of the 5 Major Risk Factors and Precursor Symptoms of Ovarian Cancer!
Ovarian cancer is a malignant tumor, and it is also the most lethal disease among gynecological cancers. Since ovarian cancer has few symptoms in its early stages, there is no obvious reason for examination. Usually, you have to wait until the ovarian tumor exceeds 10 centimeters before you can feel it from the abdomen. , and it is almost too late to diagnose ovarian cancer. However, in recent years, medical science has made great progress, and with targeted therapy, the survival rate of patients with terminal ovarian cancer has reached as high as 40%. We will take you to understand the causes of ovarian cancer, the five high-risk factors, and how to prevent ovarian cancer.
What are the causes of ovarian cancer?
Because the symptoms of ovarian cancer are difficult to detect, and the medical community is currently unclear about the cause of ovarian cancer, there have been important discoveries about ovarian cancer in recent years, that is, scientists have discovered that ovarian cancer begins in cells at the end of the fallopian tube, which means that the lesions are not necessarily It is produced in the ovary, and these new medical knowledge may shed some light on future research directions for ovarian cancer.
At present, the medical community has the following inferences about the causes of ovarian cancer:
- Number of ovulations
Some studies suggest that both pregnancy and taking birth control pills can reduce the risk of ovarian cancer. Under these two conditions, the ovaries will reduce the number of ovulations, so the researchers speculate that there is a certain correlation between the risk of ovarian cancer and the number of ovulations. During each ovulation process in women, the rupture and repair of ovarian tissue may induce abnormal cell proliferation. Rising hormone levels during ovulation can also stimulate the growth of abnormal cells. - Ligation and hysterectomy
Other studies have found that tubal ligation and hysterectomy can reduce the risk of ovarian cancer. The medical community has concluded that the risk factors for ovarian cancer travel from the vagina through the uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries. These surgeries can basically cut off the path of carcinogens. - Gene changes associated with ovarian cancer
Inherited gene mutations: When the two tumor suppressor genes (Tumor-suppressor genes) BRCA1 and BRCA2 are mutated, the risk of breast cancer and ovarian cancer increases. Acquired genetic mutations.
Most genetic mutations linked to ovarian cancer are not congenital but are caused by radiation or cancer-causing chemicals. However, no studies have found a clear link between chemicals in the environment or diet and genetic mutations that cause ovarian cancer.
4 major signs and symptoms of ovarian cancer
Although the early symptoms of ovarian cancer are not obvious, there are still signs to follow. You can pay attention to the following symptoms:
- Lose weight
- You’ll feel full quickly after eating a little something
- Often feel bloated or feel like your belly is getting bigger
- Frequent urination
In addition to the above symptoms, indigestion, nausea, etc. may also occur due to abdominal compression. However, these symptoms are quite vague and are often ignored. Therefore, no matter what kind of symptoms occur, a doctor must be diagnosed for early prevention.
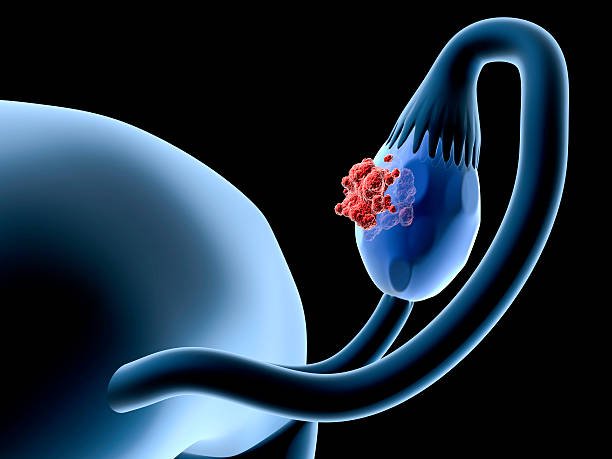
5 major risk factors for ovarian cancer self-examination
- Age:
Ovarian cancer often occurs in menopausal women or women aged 50 to 75. The older you are, the higher the risk of cancer. - Late childbearing or never having children:
Women who have their first child after the age of 35 or who have never been pregnant are at higher risk of ovarian cancer. - Have a history of cancer:
If you have a history of breast cancer, ovarian, breast and colorectal cancer or if someone in your family has suffered from similar diseases, your chances of getting cancer will be greatly increased. - Smoking:
Drug addicts have higher levels of Carcinoembryonic Antigen (CEA) than non-smokers, and CEA is related to the development of cancer. High levels of CEA are also found in other cancers, such as colorectal, lung, breast, liver, pancreatic, and prostate cancers. - Eating habits:
Women who like to eat high-fat foods and do not consume enough fiber will also have an increased chance of suffering from ovarian cancer. Research shows that those who drink full-fat milk powder are 2.6 times more likely to develop ovarian cancer than those who only drink low-fat milk powder.
How to prevent ovarian cancer?
Ovarian cancer is known as the silent killer of women. 75% of ovarian cancer patients are usually in the terminal stage when diagnosed, and the mortality rate is quite high. You can prevent ovarian cancer early by understanding the following methods:
Taking birth control pills: Taking birth control pills can reduce the risk of ovarian cancer by up to 40%. The longer you use it, the higher the risk of cancer. However, it should be noted that taking birth control pills may increase the risk of breast cancer.
- Gynecological surgery: including fallopian tube ligation and hysterectomy.
- Genetic testing: If you have a family history, genetic testing may be considered.
- Eat a balanced diet and avoid excessive fat intake in your daily diet.
- Maintain moderate exercise.
- Keep your emotions stable and pay attention to relieve mental stress.
- Women with long-term ovarian dysfunction need active treatment.