Dizziness, Blurry Eyes, or Stroke? A Look At the 7 Major Signs of Carotid Artery Stenosis and How to Improve It
Many people think that stroke is difficult to prevent and “if you encounter it, you have encountered it.” However, in fact, as long as you pay attention to certain signs in advance, you can treat it early and avoid stroke. Carotid artery stenosis is one of the most common causes of stroke; according to research, 10 to 20% of the 30,000 to 40,000 ischemic stroke patients each year are caused by carotid artery stenosis.
Common symptoms of carotid artery stenosis include dizziness and blurred vision. Since they are similar to symptoms of general anemia and physical fatigue, most people often ignore them and miss good treatment opportunities. What exactly causes carotid artery stenosis? How to avoid carotid artery stenosis? This article will explain the relationship between carotid artery stenosis and stroke, what are the 7 major signs of carotid artery stenosis, what are the symptoms, and how to treat it, so that you can understand and avoid the threat of stroke at once.
Carotid artery: one of the main arteries that supplies blood from the heart to the brain
All human organs require blood to provide oxygen and nutrients to maintain their function. Without blood flow, the organs will suffer from oxygen deprivation and necrosis, and the same goes for the brain. The blood sources of the brain are the carotid artery and the vertebral artery. If these two arteries have problems such as stenosis or blockage, the brain will face an ischemic crisis, necrosis within minutes, and lead to ischemic stroke.
The main cause of carotid artery stenosis: arteriosclerosis
Long-segment carotid stenosis is mostly caused by atherosclerosis. There is an intima inside the blood vessels. As we age and oil accumulates, the intima gradually thickens, forming atherosclerotic plaques. Atherosclerosis is also one of the main causes of many cardiovascular diseases, such as coronary heart disease, angina pectoris, myocardial infarction, etc., which are all caused by atherosclerosis and should not be taken carelessly.
Another common cause of carotid artery stenosis is thrombus exfoliation. There are blood clots in the blood, which are mainly responsible for coagulation. When the blood becomes thicker due to factors such as high blood pressure, diabetes, arteriosclerosis, smoking or obesity, the blood clots can easily accumulate in the blood vessels, leading to arterial stenosis and stroke risk.
Other causes of carotid stenosis include intimal dissection, arteritis, and psychogenic embolism
Dizziness and blurry eyes! 7 major signs and symptoms of carotid artery stenosis
Carotid artery stenosis can be divided into symptomatic and asymptomatic. Asymptomatic carotid artery stenosis refers to the occurrence of carotid artery stenosis without any discomfort, which can only be known through blood vessel examination; symptomatic carotid artery stenosis refers to the occurrence of carotid artery stenosis within six months. The following symptoms:
- Dizziness
- Soreness and stiffness in neck
- Blurred vision and total darkness (temporary amaurosis)
- Difficulty concentrating, temporary amnesia
- Slurred speech, inability to speak
- Asymmetrical expression
- Unilateral numbness and weakness in hands and feet
The above symptoms usually return to normal within 1 day. In severe cases, they may cause temporary cerebral ischemia or stroke, resulting in hemiplegia and blindness.
8 risk factors for carotid artery stenosis
Carotid artery stenosis is highly correlated with atherosclerosis. Therefore, in addition to age, which cannot be ignored, the following eight risk factors will also significantly increase the chance of carotid artery stenosis.
- Smokes
- Hypertension
- Hyperlipidemia
- Diabetes
- Obesity
- Lack of exercise
- Bad eating habits
- Have had myocardial infarction or coronary artery-related diseases
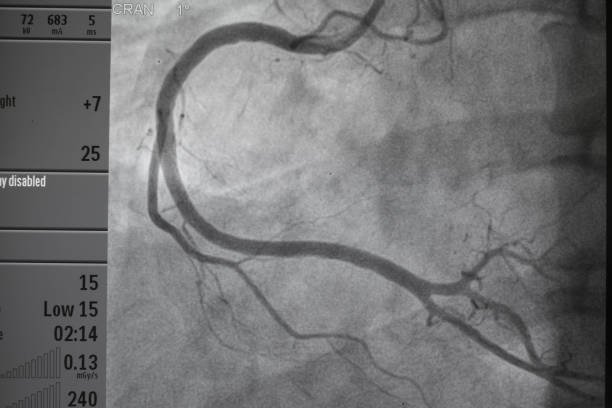
3 major examination methods for carotid artery stenosis
If you have experienced symptoms of dizziness or black vision within six months, and you are in the high-risk group mentioned above, it is recommended to seek medical treatment immediately to avoid delaying treatment or even causing a stroke. The doctor will arrange the following examinations depending on the condition:
- Neck ultrasound:
It is the most convenient non-invasive diagnostic tool. It can examine the degree of vascular stenosis and blood flow changes in the neck. The disadvantage is that it is difficult to detect the stenosis of blood vessels in the brain. - Computed tomography and magnetic resonance angiography:
are less invasive and can detect most carotid artery stenosis. If performed together with neck ultrasound, it can be more accurate than traditional angiography. - Traditional angiography:
It is highly invasive, will leave wounds, and carries the risk of infection and a very low probability of stroke. However, it is extremely accurate and is currently the most important clinical diagnostic standard.
How to improve neck blood vessel obstruction? 3 major treatments for carotid artery stenosis
There are three treatment methods for carotid artery stenosis. Doctors will determine the treatment method based on the severity of symptoms:
- Drug treatment:
The main drug used to treat carotid artery stenosis is antithrombotic drugs. However, antithrombotic drugs cannot dissolve the hardened plaque in the carotid arteries. Therefore, with oral drug treatment alone, the stroke rate within 2 years is still 20~25%. - Carotid endarterectomy:
a traditional interventional treatment, for patients with carotid artery stenosis exceeding 70%, this surgery can reduce the stroke rate on the same side of the brain by 17% within 2 years; if the stenosis is between 50 and 69% , it can reduce the stroke rate within 5 years by 6.5%. The disadvantage is that patients may have a stroke during the operation, so doctors will carefully assess the patient’s risk of complications. - Carotid artery stent placement:
A new minimally invasive treatment in recent years uses a stent catheter placed in the stenosis of the carotid artery to expand the narrowed duct and allow blood to flow smoothly. Because the trauma is small and the operation time is short, it is suitable for older and weaker patients.
Learn about carotid artery stenosis in one minute!
- Among the 30,000 to 40,000 ischemic stroke patients each year, nearly 20% are caused by carotid artery stenosis.
- The carotid artery and the vertebral artery are the two major sources of blood supply to the brain. When the arteries become narrowed or blocked due to excessive oil, the brain will die due to ischemia.
- Symptoms of carotid artery stenosis include stiff neck, blurred vision, unilateral numbness of hands and feet, asymmetric expression, etc.
- Bad habits such as smoking, lack of exercise, poor eating habits, and excessive obesity will increase the incidence of carotid artery stenosis.